
However, if you at least know they're present, forearmed is forewarned if you ever have any question marks over future bowel health. Some CHPREs have no bearing on a patient’s health. The lesions occur in one or both eyes, generally originate as small dots at the optic disc and gradually become more numerous and larger in the peripheral retina. If we see CHRPEs in your retinas, we like to know in advance whether these might represent a genetic risk for your overall health. Even if there's no known family history of bowel cancer, we'll certainly discuss them with you. A common pigment spot in the retina can be associated with a hereditary form of intestinal polyps that may become cancerous. These 'bear tracks' are segmentally oriented, clearly demarcated, flat, hyper pigmented retinal lesions, often resembling animal footprints and hence the term. If you don’t have them now, you won’t have them in future. Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE) is a rare benign lesion of the retina, usually asymptomatic and detected at routine eye. Routine colonoscopy performed in the preceding year was normal. Another name is "Bear Tracks" - you’ll see why when you look at the picture. "Congenital" means you’re born with them. Grouped pigmentation - Bear Tracks 1102 x angesehen 71 year old caucasian woman with incidental finding of extensive grouped RPE hypertrophy. These freckles are called "CHRPEs", which stands for Congenital Hypertrophy of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium. This is because the genes for a certain type of bowel cancer, called Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) will often cause certain types of freckles to appear in the retina at the back of the eye. They may enlarge with time, but are not malignant.Download the Bowel Cancer factsheet (PDF).ĭuring our history-taking, we'll ask you whether you have a family history of bowel cancer.

Congenital retinal pigment epithelial hypertrophy ( CHRPE) is usually found before patients reach 30 years of age. They are typically found during routine eye examinations. Fluorescein dye is injected into a vein in the arm/hand.

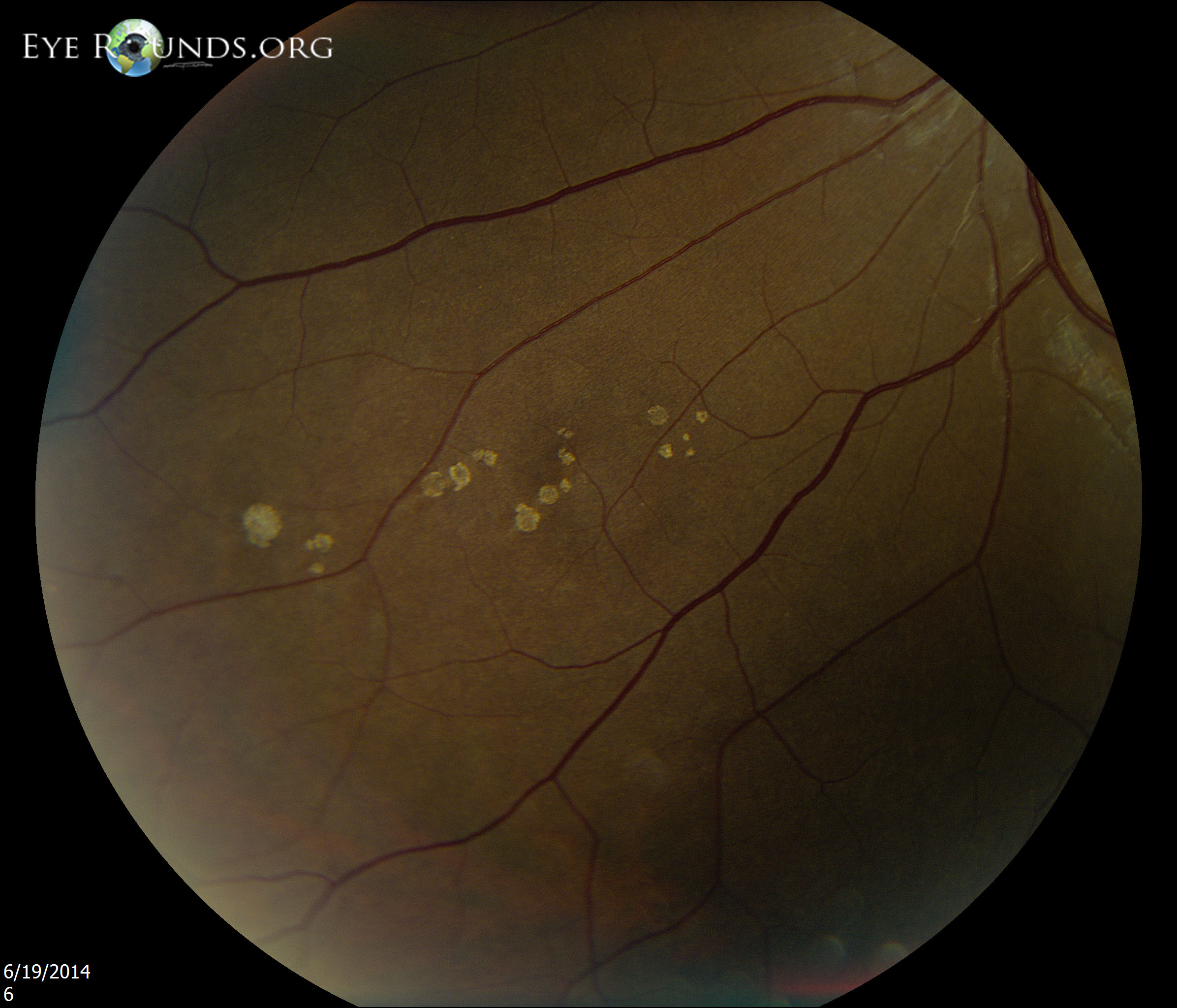
The typical isolated CHRPE represents a flat or minimally elevated pigmented, round or oval, well. The brain then sends signals throughout the body to control organs and other systems in accordance with that time of day. It’s got a 4,480-by-2,520-pixel resolution, which means it’s slightly higher than 4K. Your eyes will be dilated before the procedure. (bear tracks) or atypical multifocal CHRPE 4,5. When light enters the eye, it is sensed by a special group of cells on the retina, which is carried to the brain and interpreted as information about the time of day. Although it’s not a revolutionary innovation, the iMac’s Retina display doesn’t disappoint. This test is often used to manage eye disorders.įurthermore, how does fluorescein angiography work?įluorescein Angiography (FA) is a diagnostic procedure that uses a special camera to record the blood flow in the RETINA – the light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. The entity has also been called Melanosis Retinae, bear or animal tracks (1). These are multiple bear-track CHRPE lesions in a 38 year old lady with a strong family history of intestinal polyps and cancer. The dye highlights the blood vessels in the back of the eye so they can be photographed. Key words: Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium.
Subsequently, question is, what is intravenous fluorescein angiography? A fluorescein angiography is a medical procedure in which a fluorescent dye is injected into the bloodstream. It can be detected in an eye exam by your primary optometrist, ophthalmologist, or retina specialist. The loss of pigment allows visualization of the fluorescence created by the underlying choriocapillaris.Ībout CHRPE A flat, pigmented spot within the outer layer of the retina at the back of the eye is called a congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium ( CHRPE). A ' window defect' is an area of hyperfluorescence that occurs when there is an absence or reduction of pigmentation due to damage of the retinal pigment epithelium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
